Adelaide workplaces record dozens of electrical incidents each year, so understanding how often equipment needs inspection and tagging is critical for safety, compliance, and risk management. This guide outlines the legal framework under AS/NZS 3760:2022 and the WHS Act, details testing intervals by environment, explains who can perform inspections, breaks down costs and benefits, walks through the step-by-step Test and Tag process, and shows how businesses can stay up to date. By following these requirements, organisations minimise electric shock and fire hazards while maintaining peace of mind through professional reporting and reminder services.
What Are the Legal Test and Tag Requirements in Adelaide?
Test and Tag is mandated under the Work Health and Safety Act and AS/NZS 3760:2022 to ensure electrical safety in all SA workplaces. It requires a competent person to inspect cables, plugs, and appliances, perform electrical tests, and apply a test tag noting inspection dates. For example, businesses must schedule inspections based on risk assessments that consider environment type and usage patterns. Clear documentation and visible tagging reduce liability and support insurance requirements, laying the groundwork for sector-specific frequency rules.
What Does AS/NZS 3760:2022 Specify About Testing Frequency?
AS/NZS 3760:2022 defines minimum intervals for in-service electrical inspections based on environment and equipment use. It classifies appliances into categories such as portable, fixed, and RCDs, and mandates inspection frequencies to mitigate deterioration and electrical faults. For example, high-risk sites require three-monthly checks, while low-risk offices allow five-year intervals. Adherence to these intervals promotes ongoing electrical safety and supports systematic risk control in Adelaide operations.
How Does the WHS Act Affect Test and Tag Obligations in South Australia?
The WHS Act places a duty of care on employers to eliminate or minimise electrical hazards through regular inspection and maintenance. It requires businesses to identify risks, engage trained inspectors, and keep records of all test outcomes. Failure to meet these obligations can result in enforcement notices or fines. By embedding Test and Tag within a broader safety management plan, Adelaide organisations fulfil legal requirements and protect workers from electric shock and fire.
What Are the Specific South Australian Guidelines and Codes of Practice?
SafeWork SA and the Office of the Technical Regulator publish codes of practice that detail Test and Tag procedures, record-keeping formats, and training requirements for competent persons. They emphasise the use of portable appliance testers (PAT), visual inspections, and documented risk assessments. For instance, the SA Electrical Code of Practice outlines inspection criteria for mines, construction sites, and public venues. Complying with these codes ensures local regulatory alignment and operational consistency across Adelaide businesses.
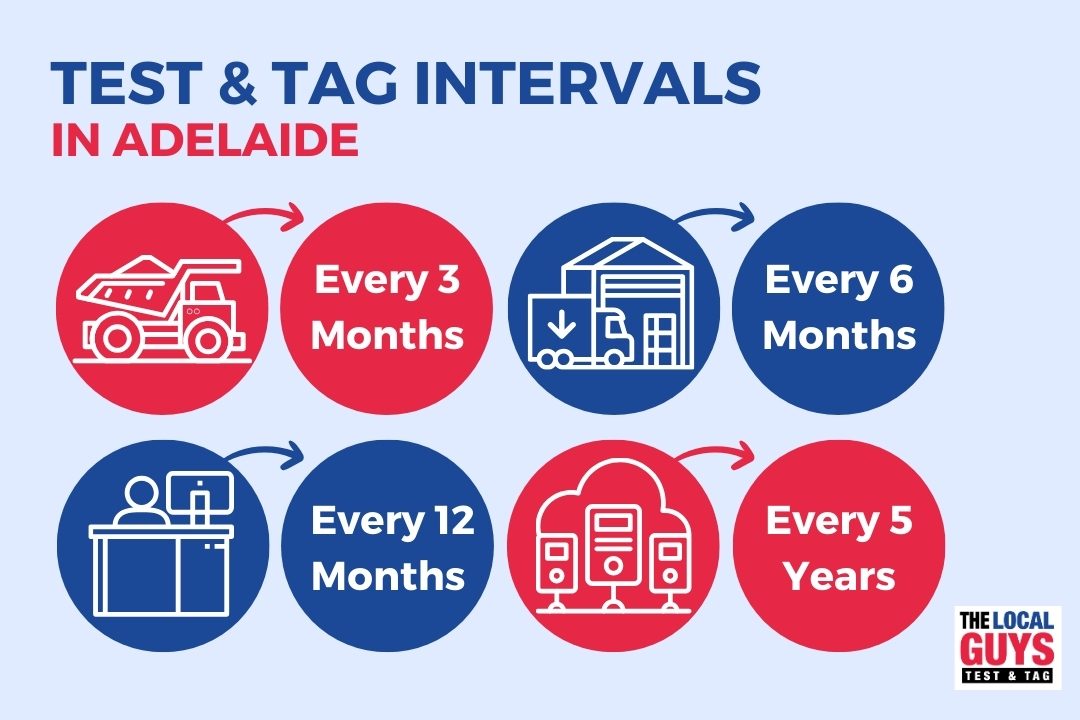
How Often Should Different Types of Electrical Equipment Be Tested in Adelaide?
Testing frequency varies according to environment risk, equipment type, and usage intensity. A structured risk-based approach evaluates potential harm and schedules inspections accordingly. Equipment that is moved, exposed to harsh conditions, or used heavily demands shorter intervals, while immobile or low-usage appliances can be tested less frequently. This ensures resources are focused where safety gains are greatest, maintaining compliance without unnecessary downtime.
What Are the Testing Intervals for Construction and High-Risk Sites?
Construction, demolition, and mining sites face rigorous electrical demands and require detailed inspections every 3 months. These intervals target environments with elevated wear and exposure to moisture or mechanical damage and prepare businesses for the next topic on moderate-risk industrial settings.
How Often Should Factories, Warehouses, and Production Equipment Be Tested?
- Factories with heavy machinery and conveyor systems require testing every six months.
- Warehouses handling forklifts, pallet jacks, and lighting systems need annual checks.
- Production lines with portable appliances demand quarterly to semi-annual inspections.
Targeting these intervals ensures sustained compliance while avoiding unplanned shutdowns, paving the way to low-risk office environments.
What Is the Recommended Frequency for Offices, Retail, and Low-Risk Environments?
- Desktop computers, printers, and desk lamps: every 12 months.
- Kitchen appliances and vending machines: every 12 months.
These extended intervals reflect minimal exposure to environmental hazards, which leads into specific requirements for residual current devices.
How Often Should Residual Current Devices (RCDs) Be Tested?
Residual Current Devices provide critical shock protection by detecting leakage currents and tripping circuits. Operator-performed test button checks should occur monthly, while full trip time tests by a competent person are required every 6 months. This dual-tier approach ensures RCDs function correctly between comprehensive inspections, reinforcing general appliance testing schedules.
What Are the Rules for Testing Hire and Second-Hand Electrical Equipment?
Hire companies and second-hand equipment suppliers must comply with both AS/NZS 3760:2022. All incoming and outgoing appliances require initial inspection before hire or sale, followed by quarterly testing during hire and annual checks once sold. This process protects end users and maintains safety integrity throughout the equipment’s lifecycle, which leads into the qualifications needed for those assessments.
Who Is Qualified to Perform Test and Tag Services in Adelaide?
Only persons who meet competency standards can perform Test and Tag services, ensuring inspections are accurate and reliable. A competent person demonstrates a clear understanding of electrical safety standards, testing procedures, and record-keeping requirements. Outlining the training pathways and licensing clarifies industry roles and prepares businesses to engage suitable providers.
What Qualifications Define a Competent Person for Test and Tag in SA?
A competent person has completed the unit of competency through a registered training organisation, covering portable appliance testing principles, electrical theory, and risk assessment. They must demonstrate practical experience or supervised assessments and hold current insurance. This certification guarantees consistency in inspection outcomes and supports broader compliance obligations.
Can Licensed Electricians Perform Test and Tag Services?
Yes, licensed electricians are authorised to conduct Test and Tag under their Statement of Electrical Work, combining fixed wiring and portable equipment safety checks. Their broader electrical licence credentials allow them to address wiring faults or RCD malfunctions discovered during PAT testing, providing an integrated safety solution that spans both portable and fixed systems.
How Is Record Keeping and Documentation Managed After Testing?
Accurate documentation underpins compliance and audit readiness. Test tags display appliance details, test date, and next due date, while logbooks or digital databases record test results, risk assessments, and inspector comments. Digital record-keeping platforms also trigger reminder services, ensuring no scheduled inspection is overlooked and supporting continuous safety management.
What Are the Costs and Benefits of Test and Tag Services in Adelaide?
Investing in professional Test and Tag services delivers measurable safety and compliance returns. Understanding cost drivers and benefits helps businesses choose the right provider and justify the investment. These insights inform value-based decision making and transition naturally into the detailed cost factors that influence pricing.
What Factors Influence the Cost of Test and Tag Services in Adelaide?
Several factors determine service fees:
- Volume of electrical appliances and number of test points.
- Environment classification and associated risk level.
- Travel distance and site accessibility.
- Testing frequency and reporting requirements.
Transparent quotes based on these criteria help organisations budget accurately, leading to recognition of the broader benefits of professional services.
How Do Professional Test and Tag Services Improve Workplace Safety and Compliance?
Safety testing identifies hidden faults such as insulation breakdown, earth leakage, and damaged leads, preventing electric shock and fire. Comprehensive reporting provides evidence of due diligence, reduces legal liability, and supports insurance claims. By outsourcing to certified providers, businesses reinforce safety culture and safeguard employees and assets.
How to Choose the Right Test and Tag Provider in Adelaide?
Selecting a reliable provider hinges on key criteria:
- Certified technicians with UEERL0003 accreditation or electrician’s licence.
- Comprehensive insurance coverage and clear service guarantees.
- Detailed reporting formats and reminder services.
- Local Adelaide expertise and responsive customer support.
Prioritising these attributes ensures quality service delivery and aligns with long-term safety strategies, which underscores the risks of non-compliance.
What Are the Consequences of Non-Compliance with Test and Tag Regulations?
Ignoring Test and Tag requirements can lead to substantial fines under the WHS Act, voided insurance policies, legal liabilities for workplace injuries, and unplanned downtime from electrical failures. Adopting systematic inspections mitigates these risks and delivers ongoing cost savings compared to reactive maintenance.
What Is the Step-by-Step Process for Test and Tag in Adelaide?
A structured Test and Tag process ensures each appliance is safe and compliant. It begins with a detailed visual inspection, proceeds through electrical testing with PAT equipment, and concludes with accurate tagging and record entry. Understanding these stages helps businesses prepare for on-site visits and supports seamless safety workflows.
How Is the Visual Inspection Conducted During Test and Tag?
The visual inspection checks for damage to cables, plugs, casings, and labels. Inspectors verify correct wiring, secure connections, and absence of overheating marks. Identifying visible defects early prevents dangerous electrical faults and sets the stage for technical testing using specialised equipment.
What Electrical Tests Are Performed Using Portable Appliance Testers (PAT)?
Portable appliance testers conduct multiple tests to verify safety:
| Test Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Earth continuity | Confirms protective earth path |
| Insulation resistance | Detects current leakage risk |
| Polarity check | Verifies correct wiring |
| Leakage current test | Measures stray currents |
These precise measurements confirm appliance integrity before a test tag is applied, leading into how tagging works.
How Are Test Tags Applied and What Information Do They Display?
Test tags are affixed next to power inlets, displaying:
- Appliance or asset ID
- Test date and next due date
- Inspector’s name or ID
- Test category and risk rating
Clear tag information facilitates quick verification during toolbox talks and audits, reinforcing traceability throughout the equipment lifecycle.
How Can Adelaide Businesses Stay Compliant with Test and Tag Requirements?
Ongoing compliance requires proactive scheduling, digital tools, and regulatory awareness. By integrating risk assessments, reminder services, and industry updates, businesses maintain uninterrupted safety management. This approach minimises lapses and aligns inspection cycles with evolving standards.
How Does Risk Assessment Influence Testing Frequency?
A risk assessment evaluates factors such as environmental exposure, usage intensity, and damage likelihood. Higher-risk appliances receive shorter inspection intervals, while lower-risk items follow standard schedules. Embedding risk-based planning ensures testing resources focus where hazards are greatest and optimises safety budgets.
What Role Do Reminder Services and Digital Record Keeping Play?
Digital reminder services automate scheduling of upcoming inspections and flag overdue tests. Cloud-based record keeping centralises test results, risk assessments, and asset histories, enabling swift audit responses and seamless handover between safety managers. This technology reduces administrative burden and fortifies ongoing compliance.
How Are Updates to AS/NZS 3760:2022 and WHS Regulations Communicated?
Regulatory updates are announced via government gazettes, SafeWork SA bulletins, and industry newsletters. Subscribing to official feeds from Standards Australia and SafeWork SA ensures businesses receive timely information on changes to testing intervals, coding practices, and competence requirements. Staying informed supports swift process adjustments and continuous legal alignment.
What Equipment Needs to Be Tested and Tagged in Adelaide Workplaces?
Organisations must identify all portable appliances and devices that connect to mains power, ensuring no items are overlooked. Covering portable, fixed, and safety-critical equipment supports a comprehensive electrical safety management plan, which maximises protection across every workplace corner.
Which Portable Electrical Appliances Require Testing?
- Power tools such as drills, saws, and grinders
- Extension leads and power boards
- Office equipment including computers, printers, and monitors
- Kitchen appliances like kettles and microwaves
Addressing these devices prevents common fault sources and links to fixed installation requirements.
Are Fixed Electrical Equipment and RCDs Included in Test and Tag?
Fixed equipment such as ovens, water heaters, and machinery with flexible cords also requires inspection under AS/NZS 3760:2022. RCDs are tested both monthly by operators and comprehensively every 6–12 months by competent persons in accordance with electrical safety regulations. This inclusive scope ensures all electrical assets are verified for safe operation.
How Are Fire Safety and Electrical Testing Integrated?
Many service providers combine Test and Tag with fire equipment inspections—such as fire extinguishers, alarms, and emergency lighting—on the same schedule. Coordinating these safety services minimises disruption, consolidates compliance reporting, and strengthens overall workplace protection strategies across Adelaide sites.
Compliance with Test and Tag requirements not only fulfils legal duties but directly reduces the risk of electric shock and fire in Adelaide workplaces. By following AS/NZS 3760:2022, engaging qualified inspectors, and leveraging digital tools, businesses can focus on core operations with confidence. Proactive risk management and professional reporting deliver regulatory peace of mind while preserving asset integrity. Regular review of standards and codes ensures inspection programmes remain aligned with the latest safety expectations.
Make a Booking Today
Contact Test and Tag Adelaide for a free quote within 2 business hours. The Local Guys help clients across South Australia with a range of fire and electrical safety testing services. If you want peace of mind knowing your workplace is secure and compliant, then get in touch with our Adelaide technicians!




